Facts about blood needs
- Every year our nation requires
about 4 Crore units of blood, out of which only a meager
40 Lakh units of blood are available.
- The gift of blood
is the gift of life. There is no substitute for human blood.

- Every two seconds someone
needs blood.
- More than 38,000 blood
donations are needed every day.
- A total of 30 million blood
components are transfused each year.
- The average red blood cell
transfusion is approximately 3 pints.
- The blood type most often
requested by hospitals is Type O.
- Sickle cell patients can
require frequent blood transfusions throughout their lives.
- More than 1 million new people
are diagnosed with cancer each year. Many of them will need blood, sometimes
daily, during their chemotherapy treatment.
- A single car accident victim
can require as many as 100 units of blood
Facts about
the blood supply
- Blood cannot be manufactured –
it can only come from generous donors.

- Type O-negative blood (red
cells) can be transfused to patients of all blood types. It is always in great
demand and often in short supply.
- Type AB-positive plasma can be
transfused to patients of all other blood types. AB plasma is also usually in
short supply.
Facts about
the blood donation process
- Donating blood is a safe
process. A sterile needle is used only once for each donor and then discarded.

- Blood donation is a simple
four-step process: registration, medical history and mini-physical, donation
and refreshments.
- Every blood donor is given a
mini-physical, checking the donor's temperature, blood pressure, pulse and hemoglobin
to ensure it is safe for the donor to give blood.
- The actual blood donation
typically takes less than 10-12 minutes. The entire process, from the time you
arrive to the time you leave, takes about an hour and 15 min.
- The average adult has about 10
units of blood in his body. Roughly 1 unit is given during a donation.

- A healthy donor may donate red
blood cells every 56 days, or double red cells every 112 days.
- A healthy donor may donate
platelets as few as 7 days apart, but a maximum of 24 times a year.
- All donated blood is tested
for HIV, hepatitis B and C, syphilis and other infectious diseases before it
can be transfused to patients.
Facts
about blood and its components
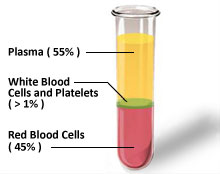
- Blood makes up about 7 percent
of your body's weight.
- There are four types of
transfusable products that can be derived from blood: red cells, platelets,
plasma and cryoprecipitate. Typically, two or three of these are produced from
a unit of donated whole blood – hence each donation can help save up to three
lives.
- Donors can give either whole
blood or specific blood components only. The process of donating specific
blood components – red cells, plasma or platelets – is called apheresis.
- One transfusion dose of
platelets can be obtained through one apheresis donation of platelets or by
combining the platelets derived from five whole blood donations.
- Donated platelets must be used
within five days of collection.
- Healthy bone marrow makes a
constant supply of red cells, plasma and platelets. The body will replenish
the elements given during a blood donation – some in a matter of hours and
others in a matter of weeks.
Facts about
donors
- The number one reason donors
say they give blood is because they "want to help others."
- Two most common reasons cited
by people who don't give blood are: "Never thought about it" and "I don't like
needles."
- One donation can help save the
lives of up to three people.

- If you began donating blood at
age 18 and donated every 90 days until you reached 60, you would have donated
30 gallons of blood, potentially helping save more than 500 lives!
- Only 7 percent of people in
India have O-negative blood type. O-negative blood type donors are universal
donors as their blood can be given to people of all blood types.
- Type O-negative blood is
needed in emergencies before the patient's blood type is known and with
newborns who need blood.
- Thirty-five percent of people
have Type O (positive or negative) blood.
- 0.4 percent of people have
AB-blood type. AB-type blood donors are universal donors of plasma, which is
often used in emergencies, for newborns and for patients requiring massive
transfusions.
There are four main blood types:
A, B, AB and O.
In 1901, Karl Landsteiner, an
Austrian physician, discovers the first three human blood groups. On his
birthday i.e June 14th "World Blood Donors Day" celebrates. On October 1st
‘National Blood Donation Day’ celebrates in India.
WHAT TYPE ARE YOU?
|
FREQUENCY OF BLOOD
TYPES
|
| O+ 1 person in 3 |
O- 1 person in 15 |
| A+ 1 person in 3 |
A- 1 person in 16 |
| B+ 1 person in 12 |
B- 1 person in 67 |
| AB+ 1 person in 29 |
AB- 1 person in 167 |
|
EXAMPLES OF BLOOD USE
|
| 1. Automobile Accident |
50 units of blood |
| 2. Heart Surgery |
6 units of blood / 6 units
of platelets |
| 3. Organ Transplant |
40 units of blood / 30 units
of platelets |
| 4. 20 bags of
cryoprecipitate |
25 units of fresh frozen
plasma |
| 5. Bone Marrow Transplant |
120 units of platelets/ 20
units of blood |
| 6. Burn Victims |
20 units of platelets |






